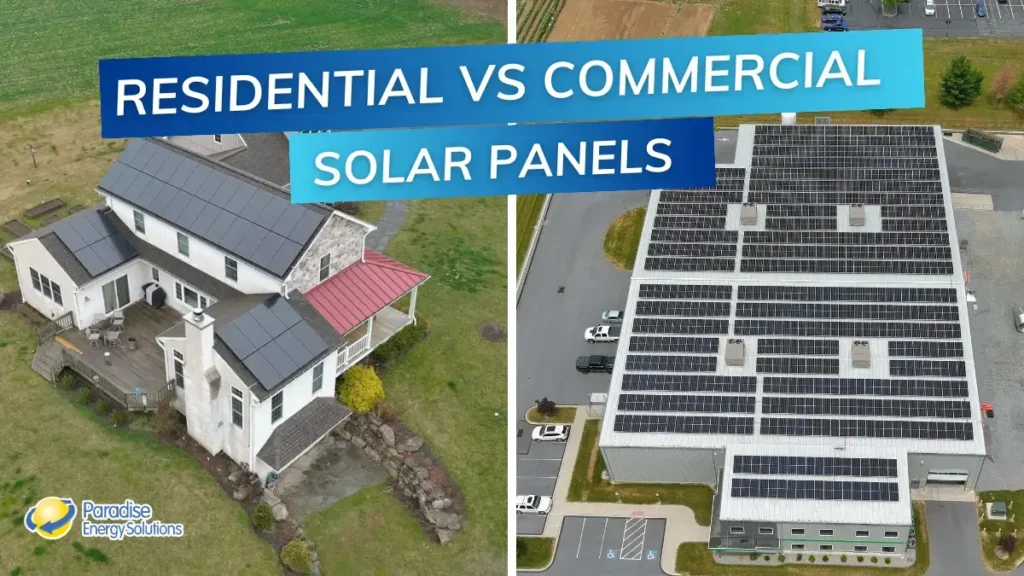
Whether you are considering installing solar panels for your home or business, it is important to understand the key differences between residential and commercial solar panels.
In this blog, we will explore the variations in size, design, warranty, and other factors that set these two types of solar panels apart.
What Sets Commercial and Residential Solar Panels Apart?
The Size
One primary distinction between residential and commercial solar panels is their size. Commercial solar panels are typically larger than their residential counterparts, substantially increasing surface area and energy production capabilities.
Residential solar panels, measuring approximately 45” x 70”, are designed to cater to the energy needs of individual homes. These smaller panels are well-suited for rooftop installations and blend seamlessly into the aesthetics of residential properties.
Commercial solar panels, measuring around 45” x 90”, are designed for commercial buildings and large businesses. Their increased size allows them to generate more power to meet the high energy requirements of commercial spaces.
Design Considerations
Another significant difference between residential and commercial solar panels lies in their design.
 Residential solar panels often prioritize aesthetics. Most feature an all-black design that integrates seamlessly with the home’s appearance. These panels are typically monofacial, generating electricity from one side, and are designed to be visually pleasing while adequately meeting the energy needs of most households.
Residential solar panels often prioritize aesthetics. Most feature an all-black design that integrates seamlessly with the home’s appearance. These panels are typically monofacial, generating electricity from one side, and are designed to be visually pleasing while adequately meeting the energy needs of most households.
 On the other hand, commercial solar panels tend to prioritize function over aesthetics. The frames of commercial panels are frequently silver and more utilitarian in appearance, reflecting their primary role in maximizing energy production rather than blending into the building design.
On the other hand, commercial solar panels tend to prioritize function over aesthetics. The frames of commercial panels are frequently silver and more utilitarian in appearance, reflecting their primary role in maximizing energy production rather than blending into the building design.
In terms of functionality, these panels can be either monofacial or bifacial. Monofacial panels, which generate electricity from one side, are more commonly installed in commercial and agricultural settings due to their efficiency and cost-effectiveness. These panels are best suited for metal and shingle roofs.
Bifacial panels, capable of generating power from the top and bottom sides of the panel, are also used in certain commercial applications where they can utilize reflected sunlight to increase energy production. This is a common sight on flat roofs, where ballast mount systems position the panels at an angle to maximize the capture of sunlight’s reflection on the underside.
Warranty Coverage
Warranty coverage plays a pivotal role in solar panel investments’ long-term value and reliability, so let’s dive into the differences between commercial and residential solar panel warranties.
Commercial Solar Panels: Product Warranty
Commercial solar panels generally come with a product warranty ranging from 12 to 15 years. This warranty ensures that any defects or malfunctions in the panels will be repaired or replaced within the specified period.
Residential Solar Panels: Product Warranty
Residential solar panels often come with a longer product warranty of 25 years. This extended warranty gives homeowners peace of mind, knowing that their investment is protected for the majority of the system’s life.
Production Warranty: A Common Ground
Despite these differences in product warranty lengths, residential and commercial solar panels typically share a common feature in their production warranty. This warranty:
Guarantee Energy Output (Linear Warranty): This ensures that the solar panels will produce a certain percentage of their rated power output for at least 25 years.
For example:
| Solar Panel Brand | Residential | Commercial |
| Qcells Solar Panels |
At least 98.5% of nominal power during the first year. At least 90.58% of nominal power up to 25 years. |
At least 98% of nominal power during the first year. At least 84.95% of nominal power up to 30 years. |
| Axitec Solar Panels |
At least 97% of nominal power during the first year. At least 85% of nominal power up to 25 years. |
At least 97% of nominal power during the first year. At least 85% of nominal power up to 25 years. |
| SEG Solar Panels |
At least 98% of nominal power during the first year. At least 84.8% of nominal power up to 25 years. |
At least 98% of nominal power during the first year. At least 84.8% of nominal power up to 25 years. |
Understanding Solar Panel Costs: Residential vs. Commercial
When considering the installation of solar panels, it’s important to understand the cost dynamics at play. The pricing structure for solar panels does vary between residential and commercial installations, influenced by factors such as the type of panel and economies at scale.
Residential Solar Panel Costs
- Price Range: Residential solar panels typically range from $2.70 to $4.00 per watt. The average cost, before incentives, hovers around $2.70 per watt.
- Factors Influencing Cost: In residential settings, factors like the complexity of the installation, the type of roof cover, the height of the building, the steepness of the roof, the scale of the purchase, and additional costs like underground trenching contribute to the overall system cost.
- Incentives and Rebates: Homeowners can offset these costs through various incentives, such as the federal tax credit and solar renewable energy credits (SRECs).
Commercial Solar Panel Costs
- Average Cost: Commercial solar panels have an average cost of $2.30 per watt, notably lower than residential solar panels.
- Factors Influencing Cost: This price difference primarily reflects the economies of scale. Larger commercial installations purchase more equipment and can spread the installation and labor costs over a larger system, reducing the cost per watt.
- Incentives and rebates: Commercial solar installations benefit from multiple financial incentives that help offset the installation cost. Key among these are the tax benefits of the federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) and accelerated depreciation, which provide substantial tax savings. The USDA REAP Grant also helps rural businesses recoup much of the installation cost.
Final Thoughts: Choosing Between Residential and Commercial Solar Panels
As we wrap up, this comparison between residential and commercial solar panels highlights how each is uniquely tailored to meet different energy requirements.
Residential Solar Panels: Suited for homes, these panels are typically smaller and monofacial, with longer product warranties. They are designed to integrate seamlessly onto residential rooftops, effectively meeting household energy needs.
Commercial Solar Panels: Built for business needs, these panels are larger, can be monofacial or bifacial, and usually come with shorter warranties. Their design is geared towards handling the larger energy demands of commercial facilities.
Whether your interest lies in residential or commercial solar panels, the decision hinges on factors like energy requirements, available space, and design preferences.
Considering solar energy for your property? Get in touch with us today to discuss your options and begin your journey towards big savings.